A Model Used to Describe How Enzymes Function
Which model is sometimes used to describe enzyme-substrate interactions. What best describes the function of enzymes.
Enzymes A Level The Science Hive
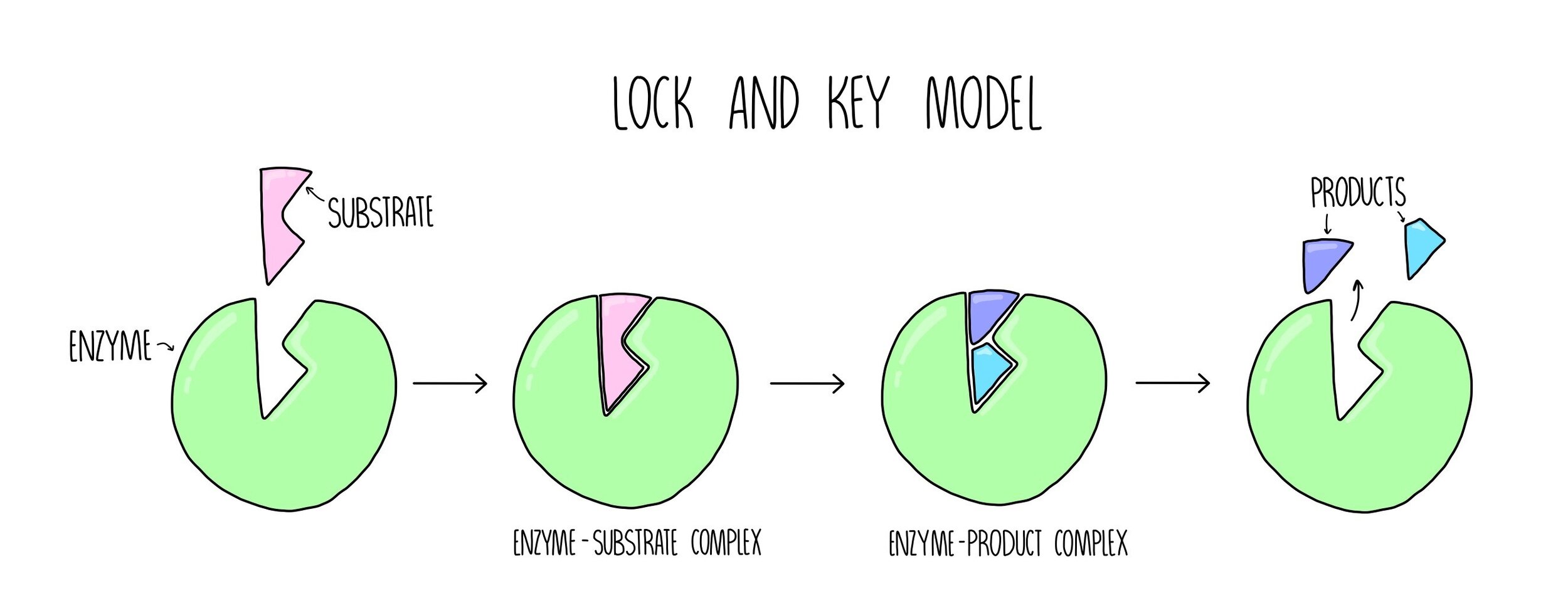
As with a lock and the key that opens it the shapes must be complementary and this shape can not change.
. This concept was given by biologist Emil Fisher in his lock and key structure model. Click on the mouse at left to clear the images and text. The lock and key model also called Fishers theory is one of two models which describe the enzyme-substrate interaction.
The substrate and enzyme complement each other. The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. Part 1 Day 1 2.
Enzymes are lifes great facilitators. In lock and key the enzyme is the lock and the substrate is the key. The two models to explain the actions of enzymes with substrates are the Lock and Key model Induced fit model.
The key substrate has a specific shape arrangement of functional groups and other atoms that allows it and no other key to fit into the lock the enzyme. What term is used to describe enzymes which work outside the cell. Enzymes are biological catalysts--they catalyze the chemical reactions that happen inside living things.
The two principal models for allosteric enzyme behavior are called the concerted model and the sequential model. Students can be divided in groups of 2 or 3. Similar to how a key has to be the correct one for a lock no reaction takes place if an incorrect substrate tries to bind.
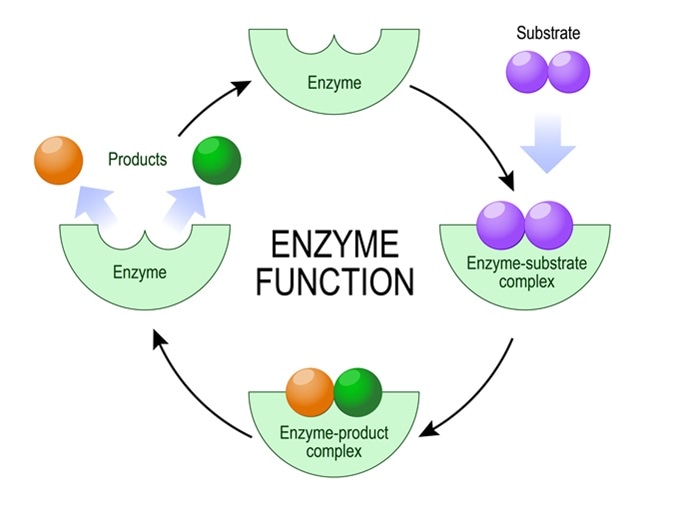
Now sometimes things will bind to enzymes at places other than their active sites. Formation of Enzyme-substrate Complex. In a model of enzyme action the enzyme can attach only to a substrate reactant with a specific shape.
A _____ is a biological catalyst. Catabolism _____ refers to the decomposition of complex compounds during cellular metabolism usually with the release of energy. The objective of this activity is to introduce the concept of enzymes and their functions through the lock-and-key model by using real locks and keys as an analogy.
It possesses a unique shape that complements that of the substrate. And we call this allosteric binding. Arrows point to the active sites of the enzyme 2.
The active site of an enzyme is a specific region that receives the substrate. Just like a lock and key the enzyme as the lock and the substrate as the key is said to fit together. 1 The lock and key model.
The surface configuration of the active site is such as to allow the particular substrate molecules to be held over it. 2 The induced fit model. The enzyme-substrate interaction in the lock-and-key paradigm implies that the enzyme and the substrate have complimentary geometric forms that fit perfectly together.
In the induced-fit model the active site. The general name that chemists use for a chemical entity that increases the speed of a reaction is a catalyst. The _____ site is the region on an enzyme that binds substrate.
In the lock-and-key model the active site of an enzyme is precisely shaped to hold specific substrates. Enzyme lock and key model The lock and key model was first proposed in 1894. The Lock-and-key mechanism was first proposed by Emil Fischer which described as the enzymatic reactions whereby an enzyme with a single substrate binds temporarily to form a substrate complex.
They create the conditions needed for biochemical reactions to happen fast. It was proposed that the shape of the enzyme. The enzyme then changes and reduces the activation energy of the reaction so reactants can.
So enzymes dont necessarily bind just to one substrate. Usage michaelis compet_mich non_compet_mich. Michaelis-Menten model and derived equations to model competitive and non-competitive inhibition Description.
Enzyme models are used to try and describe the general mechanism that enzymes use to process substrates into new products. This illustrations depicts the colormagentalock and key model of enzyme and substrate binding first proposed by Emile Fischer in his studies on enzymes in the nineteenth century. B Induced fit.
The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the. Click on the numbers below to see how the lock-and-key model of enzyme action works. Both enzymes and substrates have specific geometrical shapes.
Substrates bind to the active. Formula of Michaelis-Menten model commonly used to describe enzyme kinetics and derived formulas taking into account the effect of a competitive or a non-competitive inhibitor. So if we have an enzyme here with its active site a regulating molecule like an inhibitor made by the enzyme at a different location than the enzymes active site.
Procedure Part 11. In this model an enzymes active site is a specific shape and only the substrate will fit. This model states that the interaction between substrate and enzyme is weak and these weak interactions induce conformational changes rapidly and strengthen binding and bring catalytic sites close enough to substrate bonds.
The lock and key model was the first and now the outdated model used to describe the physical and molecular interaction between enzyme and substrate. The lock-and-key model refers to the way in which a substrate binds to an enzymes active site. The lock and key model assumes that the active site of the enzyme and the substrate are equal shaped.
It supposes that the substrate fits perfectly into the active site of the enzyme. The favourable model of enzyme-substrate interaction is called the induced-fit model. UlIllustration going from righ t to left 1.
Which model is sometimes used to describe enzyme substrate interactions. Substrate binds more easily to the R. Enzymes and Their Functions Lock-and-Key Activity Objective.
At the moment two models are used to describe enzyme specificity. The Induced fit model describes the formation of the E-S as a result of the interaction between the substrate and a flexible active site. The lock and key model.
This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. There are two predominant enzyme activity models. It allows better binding and catalytic effects.
In the concerted model the enzyme is thought of as being in a taut form T or a relaxed form R. The substrate produces changes in the conformation on the enzyme aligning properly the groups in the enzyme. All subunits are found in one or the other and an equilibrium exists between the T and R forms.


Comments
Post a Comment